CÉH+ BIM
With the help of our professionally prepared experts who have several years of practice and both domestic and international experience, we apply the BIM methodology at a system level and provide our related services with excellent quality.
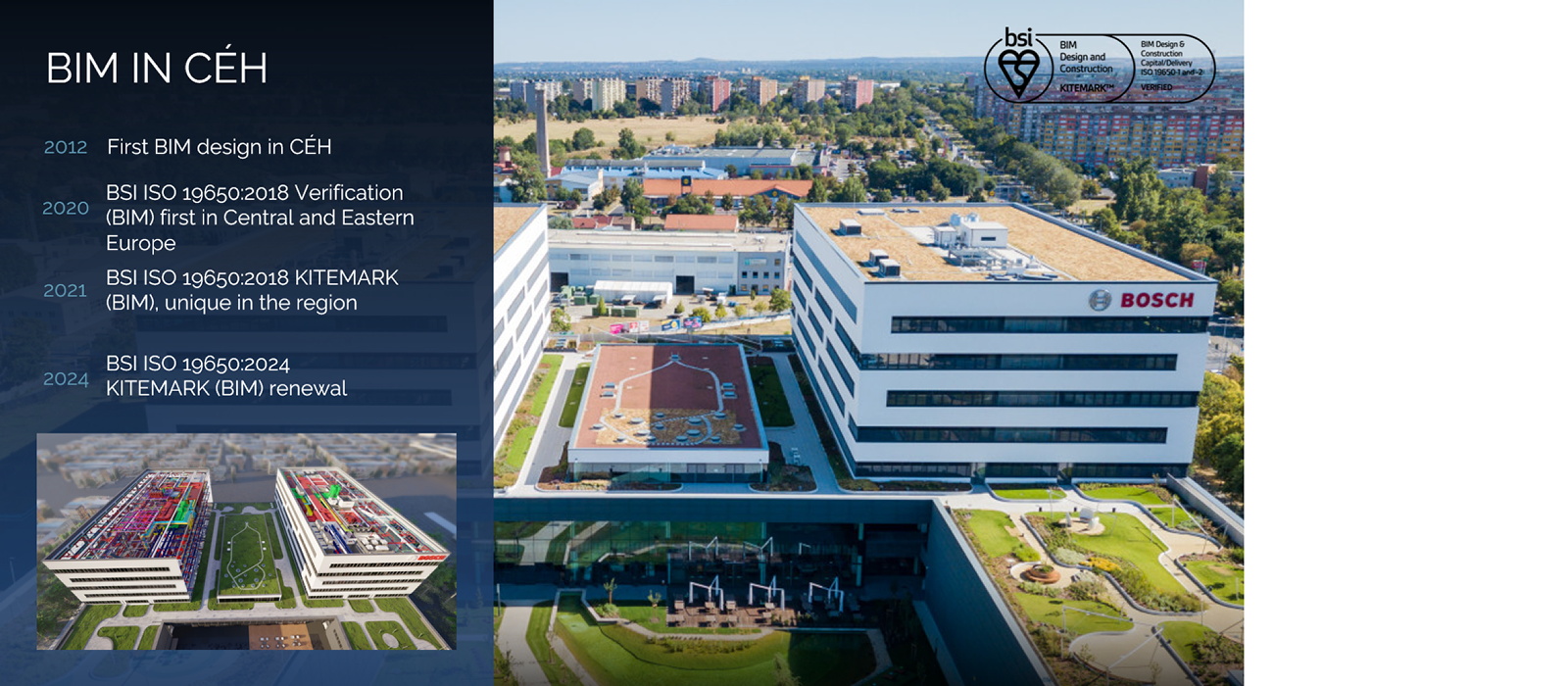
In April 2020, the CÉH group was the first in Central-Eastern Europe to obtain certification from the British Standards Institute for the application of ISO 19650-1 and -2:2018 standards, which provide guidelines for the management of information generated during the lifecycle of a building using the BIM working method. Thus, CÉH is the first market player in the region to provide BIM design, project management, and consulting services according to international standards.
Our Services
which we offer both collectively and individually:
- Our services which we offer both collectively and individually:
- Scan2BIM – 3D laser scanning and/or drone surveying of buildings and structures, creation of point cloud models, and from these, creation of BIM base models.
- Design (BIM 3D) – Comprehensive design and modeling of buildings and structures (covering all disciplines and even technologies), collision detection in BIM.
- Project management, construction management (BIM 4D) – Coordination of the investment process and technical inspection representing the client's interests during the execution of high-rise projects.
- Cost expertise, cost estimation (BIM 5D) – Quantity calculation based on BIM models, cost calculation, contractor tendering, cost control.
- Sustainability and energy expertise (BIM 6D) – Detailed energy analysis, dynamic energy modeling and thermal comfort examination, CFD simulation, sunlight analysis, wind tunnel and wind load examination, green certification (LEED/BREEAM/DGNB/WELL) planning and monitoring.
- As-built plan, BIM2FM (BIM 7D): BIM as-built model, change management, BIM model detail and data provision suitable for handover to operation.
- BIM management – Establishment and management of BIM processes.
- BIM expertise, consulting – Professional BIM representation of the client during the project, model auditing, quality control. Establishment of client standards, participation in the preparation of tenders and contracts.
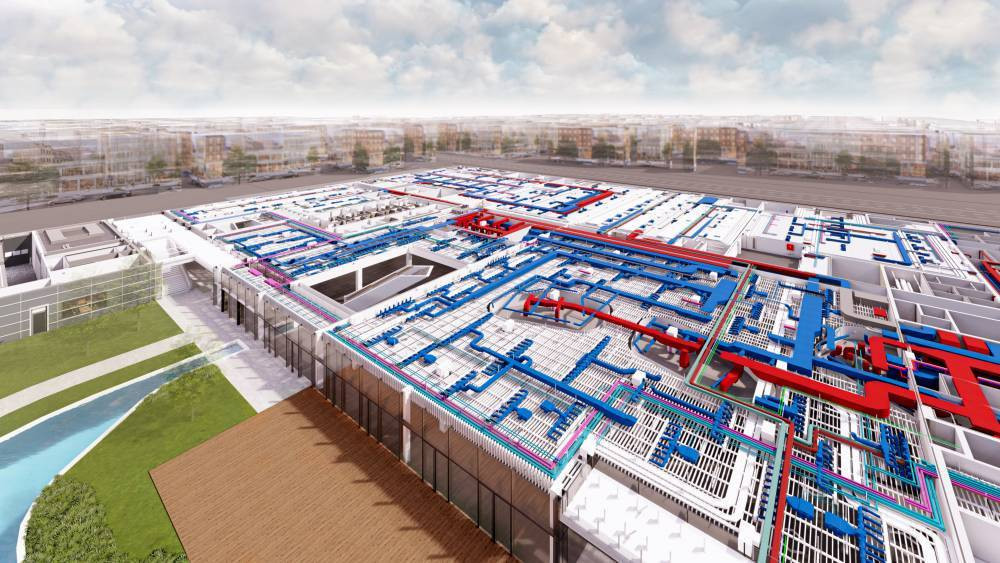
What does BIM mean?
BIM, or Building Information Modeling, is a working process for tracking the entire lifecycle of a project: from inception, through implementation and operation, to eventual demolition. Regarding the type of project, it can be a building, a bridge, a road, an engineering structure, a public utility or any civil engineering structure above ground or underground.
During the BIM process, the most advanced CAD and data exchange technologies are used in the design, construction and operation processes, facilitating model-based project design and control.
The BIM work processes are based on a 3D model created in a virtual environment, which refers to the technical content of the building and provides its geometric and structural image in space.

Why should you use BIM?
The uniform standards, regulations, shared models and information applied in the work processes improve:
- Collaboration between stakeholders (trades, project management, designers and contractors)
- The coordination of works
- The quality of the design,
- The ability to plan and monitor construction processes
- Cost planning and control.
With BIM, the project can be delivered faster, with higher quality and at a lower cost through better design.

What does the future hold?
In construction industry digitalization, we consider the BIM methodology as a starting point, which consolidates all the data of the facility into a unified database. Forward-looking approaches elevate the design and construction process to a new level.
VDC (Virtual Design and Construction) is an approach that integrates not only the building but also the construction process and the involved parties into the digital model. VDC is a process and mode of operation where construction management is based on the BIM model created during the design phase. The building is first constructed in the virtual space and then replicated in reality.
IDD (Integrated Digital Delivery) extends digital technologies to the entire lifecycle of the facility, integrating workflows and connecting the parties working on the same project. Thus, using the digital model of the building, the entire lifecycle can be digitized, from the formation and manufacturing of prefabricated elements to assembly, operation, or even disassembly.
IDD is based on the use of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Virtual Design and Construction (VDC), which have been applied in numerous construction projects abroad in recent years, and their domestic spread is also expected.
Frequently Asked Questions and Answers
1. What does BIM model-based design mean, and how does it support the return on my investment?
BIM (Building Information Modeling) model-based working means that a building or facility is described by a data-rich 3D digital model rather than only by 2D drawings. Each element in the model has associated geometric data, technical parameters, quantities and – if required – operation and maintenance information.
Thanks to this, clashes can be identified already in the design phase, accurate quantities are available for cost planning, and 4D and 5D BIM tools make it possible to simulate the construction schedule and cost changes. All this leads to fewer errors, shorter construction times and better-controlled investment costs. At CÉH, BIM models have been the fundamental tool of our design workflows for more than a decade.
Source: CÉH zRt., BIM team, last updated: January 2026.
2. What should I know about the differences between a BIM model and traditional 2D design?
In 2D design, separate drawings describe the building, and keeping them consistent relies largely on the designer’s attention. With BIM, we work in a single 3D model from which floor plans, sections and elevations are generated directly. When something is changed in the model, it is updated automatically in all related drawings. The model is made up of intelligent elements (walls, columns, MEP components) with quantity and technical data. This reduces drawing inconsistencies, speeds up design changes and provides a more reliable basis for cost and schedule planning.
Source: CÉH zRt., BIM team, last updated: January 2026.
3. How does BIM-based design differ from the traditional CAD approach?
In traditional CAD, we draw lines that together form the picture of the building, but there is relatively little structured data behind them. In BIM, we work with “intelligent” building elements: walls, columns, doors and windows, MEP equipment, each with associated material, size, performance and other information. In CÉH’s BIM-based design, the central 3D model is the single source of truth; from this, 2D drawings, quantity take-offs and simulations can be generated automatically via export. This reduces errors, speeds up changes and provides stronger decision support for the client.
Source: CÉH zRt., BIM team, last updated: January 2026.
4. What are the tangible benefits of using BIM for investors and clients?
With BIM, the client can see the project early and in an understandable form, not only on line-based drawings. More accurate quantity and cost data are available, there are fewer clashes and late design changes during construction, and the number of variations and site reworks decreases, as does the time needed for designer site support. The schedule becomes more transparent and it is easier to compare different options. CÉH’s BIM workflows also create value for construction and operation: the model can become the digital backbone for future facility management.
Source: CÉH zRt., BIM and Project Management team, last updated: January 2026.
5. When is it worth using a BIM model for an industrial project, and what is the business benefit?
For industrial projects, BIM is practically recommended for almost every case: complex halls, technological spaces, logistics connections and long-term operation. CÉH’s BIM models show spatial relationships, clashes and quantities already from the concept phase, which results in more accurate cost estimation, better schedule control and faster commissioning.
Source: CÉH zRt., BIM team, last updated: January 2026.
6. Which BIM dimensions (3D–7D) can be applied, and what are their practical benefits?
3D is the spatial model; 4D adds time (scheduling); 5D adds cost and quantities; 6D includes energy and sustainability data; 7D covers operational and facility management information. With 4D–5D BIM models, the construction sequence and costs can be planned more reliably. 6D–7D support the operator in making well-founded decisions on maintenance, refurbishment and energy use throughout the asset’s life cycle.
Source: CÉH zRt., BIM team, last updated: January 2026.
7. What does the 7D dimension of BIM mean, and how does it support facility management (FM)?
7D is the BIM model’s extension towards operation and facility management. Each element can have a maintenance cycle, warranty information, manufacturer data, energy consumption and other operational parameters attached to it. If requested by the client, CÉH’s 7D-ready models allow the operator to see at a glance which piece of equipment needs maintenance when, where it is located and which documentation belongs to it. This reduces unexpected failures and supports optimisation of life-cycle costs.
Source: CÉH zRt., BIM and FM-focused team, last updated: January 2026.
8. What does BIM certification according to ISO 19650-1 and -2 mean?
ISO 19650-1 and -2 are international standards that define the framework for BIM-based information management in the design and construction phases of the built environment. They are not tied to any specific software; instead, they define how data must be structured, handled securely, with clear responsibilities and rules between project participants. If an organisation or project follows ISO 19650-compliant processes, this means more transparent, traceable and reliable digital information flows for the client.
Source: CÉH zRt., BIM and Quality Management team, last updated: January 2026.
9. What is clash detection and 4D simulation good for, and how do they reduce construction errors?
Clash detection automatically searches the BIM model for elements that intersect or collide, for example between MEP pipes and structural elements, between cable trays and ducts, or between equipment and building components. 4D simulation adds the time dimension: it shows when each element is built and in what sequence the different trades work. If requested, CÉH performs these checks before construction starts, so most conflicts can be resolved in the digital space instead of on site by demolition. This significantly reduces errors, rework and delays.
Source: CÉH zRt., BIM team, last updated: January 2026.
10. How does 4D BIM simulation work, and what does it reveal about the construction schedule?
4D BIM simulation links the 3D model to the project schedule: each model element is given the time period when it will be built. This makes it possible to “play back” the construction process along a timeline: parallel works, congested zones and potential logistics conflicts become visible. Based on this, the schedule can be adjusted and resource allocation optimised, reducing the risk of delays.
Source: CÉH zRt., BIM and Project Management team, last updated: January 2026.
11. What types of issues can be prevented with digital clash detection?
Digital clash detection helps identify conflicts that would cause significant demolition and costs on site: intersecting MEP and electrical runs, pipes colliding with structural elements, ducts running too low, equipment that physically does not fit and installations overlapping in the same space. CÉH’s BIM team identifies these conflicts already during the design phase, so solutions are developed in the model, not during construction.
Source: CÉH zRt., BIM team, last updated: January 2026.
12. How does BIM support scheduling, cost control and the prevention of construction errors?
BIM supports scheduling in 4D and costs in 5D: time and cost data can be attached to each model element. Quantities generated from CÉH’s models enable more accurate cost estimates, while 4D simulations highlight critical phases, parallel activities and logistical issues. Clash detection reveals most installation conflicts in the digital environment. This leads to fewer errors, less downtime and reduced cost overruns during construction.
Source: CÉH zRt., BIM and Project Management team, last updated: January 2026.
13. What role do clash detection and 4D/5D BIM models play in construction planning?
Clash detection uncovers geometric conflicts in the model, while 4D links it to time (schedule) and 5D to costs. If requested, CÉH uses these models during detailed design, so the contractor receives a project where most scheduling and installation risks are already visible and manageable. This leads to more reliable tenders, fewer uncertainties and smoother construction for the client.
Source: CÉH zRt., BIM team, last updated: January 2026.
14. When is BIM-based quantity take-off needed, and how does it differ from traditional cost estimation?
BIM-based quantity take-off is particularly useful for complex, high-value projects. Traditional cost estimates are based on 2D drawings and manual quantity extraction; BIM-based quantities, in contrast, are generated directly from the model elements. When the model changes, the quantities are updated accordingly. This provides more accurate, transparent and dynamically updatable cost estimates.
Source: CÉH zRt., BIM and Cost Planning team, last updated: January 2026.
15. What methods does CÉH use for digital surveys of existing buildings?
Our main methods are terrestrial laser scanning and drone-based photogrammetry. The scanners capture dense 3D point clouds, while the drone records the exterior and hard-to-reach parts. Based on the point cloud, a 3D BIM model is created, which serves as the basis for further design and engineering analyses.
Source: CÉH zRt., Digital Survey and BIM team, last updated: January 2026.
16. How do digital building surveys (laser scanning, drones) support design and refurbishment?
A point cloud–based digital twin provides precise geometry. The BIM model is created within this space, so the design is no longer based on uncertain, outdated drawings. This reduces the number of surprises during construction and demonstrably improves the reliability of pricing and refurbishment plans.
Source: CÉH zRt., Digital Survey and BIM team, last updated: January 2026.
17. For which types of projects are drone and laser-scanner surveys recommended?
These methods are especially important where the geometry is complex, access is difficult or the asset is already in operation: industrial halls, plant rooms, heritage buildings, bridges and large industrial sites. The approach enables accurate, fast and safe data collection without extensive scaffolding or disruption.
Source: CÉH zRt., Digital Survey team, last updated: January 2026.
18. When is it worth integrating existing buildings into a BIM model using laser scanning, and how is this done?
Integrating existing buildings into BIM is particularly recommended when the facility is complex or old, drawings are incomplete, or a major refurbishment or conversion is planned. CÉH first creates a point cloud with a laser scanner (and a drone where required), then builds the BIM model from this. The model reflects the actual geometry, on which new structures and systems can be safely designed.
Source: CÉH zRt., Digital Survey and BIM team, last updated: January 2026.
19. What digital tools and developments does CÉH use to support innovative engineering services?
CÉH’s digital ecosystem includes BIM platforms, a common data environment (CDE), 4D/5D simulations, laser scanners, drones, automated quantity take-off, parametric design tools, visualisation solutions and in-house reporting and dashboard applications. Together, these tools ensure structured data, transparent collaboration and decision-ready information for our clients.
Source: CÉH zRt., Digital Development and BIM team, last updated: January 2026.
20. Why is parametric design useful for complex technical buildings?
Parametric models make it possible to test different design variants quickly and immediately see the impact of parameters such as span, module size or MEP demands. This is particularly beneficial for large industrial, infrastructure or other complex buildings with many interdependent constraints. The approach allows CÉH to compare alternatives more efficiently and support the client in selecting the most suitable solution in terms of design, cost and programme.
Source: CÉH zRt., Parametric and BIM Design team, last updated: January 2026.


